Breast Mass (Breast Cancer) The most common situation in the formation of a mass in the breast occurs with the detection of a painless mass. This is the clearest sign of breast cancer. It is possible to reach a clear conclusion as a result of examining the breast masses, since not all masses formed in the breast will be cancer. While a cancerous breast mass can be detected, a benign cancerous mass can also be detected. You can also do an individual test for the appearance of a mass in the breast. You can see a lot of things like the patient’s age, whether the mass is painful or not, the limits of stiffness. Masses and stiffness found in the 1930s and 1940s are more indicative of cysts and fibrocystic disease. Painless lump, stiffness or swelling of the breasts after age 35-40 should primarily
be a reminder of breast cancer. If more than one mass is palpable in the breast or if the mass is palpable in both breasts, fibroadenoma or fibrocystic disease should be considered first. Fibrocystic disease or fibroadenomas can sometimes cause mild pain. Breast masses that are sometimes noticed by the patient during self-examination and sometimes not detected during examination are usually insignificant. If the mass reaching the patient’s hand has a smooth surface and is mobile like marbles in breast tissue, it is likely to be benign. 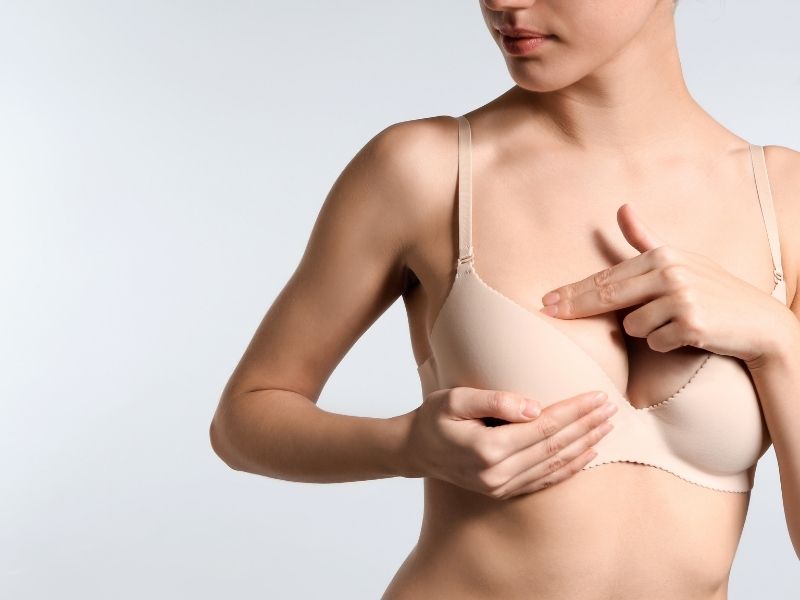 Conversely, if the surface is uneven and immobile, the likelihood of cancer is greater.
Conversely, if the surface is uneven and immobile, the likelihood of cancer is greater.
The most obvious symptom of breast cancer is a lump. These masses may be seen during manual breast inspection or during follow-up radiological examinations. Also, changes in breast tissue, skin recessions, skin redness, the appearance of veins, bloody nipple discharge, and palpable masses in the armpits show up as signs of breast cancer. However, these symptoms usually occur in advanced breast cancers. Breast cancer is a disease that occurs as a result of a tumor caused by the uncontrolled change and proliferation of one of the cell groups that make up breast tissue. As a result of this uncontrolled proliferation observed in the mammary ducts or mammary glands, similar mass and structures are formed in the breast. Cancer cells that continue to multiply rapidly afterward usually attach themselves to surrounding tissues and grow in a certain area. This mass, which can be seen from the outside as a result of the physical examination, makes it much easier to detect breast cancer than cancers of the lung, liver, stomach, and similar organs. In patients who are not diagnosed and treated in time, the cancer spreads to other organs and goes into an incurable stage. Considering the importance of early diagnosis in breast cancer and the possibility of screening, self-examination and medical examination are very important. Even if she has no complaints about her breasts, every woman should be seen by a general surgeon for a clinical breast exam every 3 years between the ages of 20 and 40 and once a year after age 40. Surgery is the most important part of breast cancer treatment. The purpose of breast cancer surgery is to remove the entire tumor from the body. Treatment methods other than surgery aim to prevent the tumor from returning (relapsing) or spreading to other organs. There are basically 3 types of surgery: mastectomy It is called removal of the entire breast along with the tumor. In the same session or in the late period (1-2 years later) to the patient; New breasts can be made with silicone implants or with your own tissues.
Skin-conserving mastectomy This is a preferred method in cases where the entire breast tissue needs to be removed but breast skin can be preserved. Instead of the removed tissue, a silicone implant is placed inside the skin to provide an aesthetic appearance. It is particularly preferred for breast cancer risk reduction surgeries (prophylactic mastectomy). Breast Preservation Surgery A surgical method in which only the tumor is removed along with some normal breast tissue around it. This surgery has two purposes: first, the aesthetic appearance of the breast is not deteriorated by leaving the breast in place; second, to ensure that the patient is affected at the lowest level, both physically and psychologically. After breast cancer surgery, radiation therapy can be applied for 5-7 weeks. mastectomy It is called removal of the entire breast along with the tumor. In the same session or in the late period (1-2 years later) to the patient; New breasts can be made with silicone implants or with your own tissues. Skin-conserving mastectomy This is a preferred method in cases where the entire breast tissue needs to be removed but breast skin can be preserved. Instead of the removed tissue, a silicone implant is placed inside the skin to provide an aesthetic appearance. It is particularly preferred for breast cancer risk reduction surgeries (prophylactic mastectomy). Breast Preservation Surgery A surgical method in which only the tumor is removed along with some normal breast tissue around it. This surgery has two purposes: first, the aesthetic appearance of the breast is not deteriorated by leaving the breast in place; second, to ensure that the patient is affected at the lowest level, both physically and psychologically. After breast cancer surgery, radiation therapy can be applied for 5-7 weeks.


